Global study finds homophobia, comfort with service provider, and community engagement make significant impact on access to condoms, lubricant, HIV testing, and HIV treatment
A large-scale study of gay men and other men who have sex with men (MSM), conducted by the Global Forum on MSM & HIV (MSMGF), indicates that only one third of MSM can easily access condoms, lubricant, HIV testing, and HIV treatment. Combining a multi-lingual online survey and focus group discussions, the study suggests that structural barriers like homophobia play a significant role in blocking access to HIV services for MSM, while greater comfort with service providers and community engagement are associated with higher levels of service access.
The MSMGF’s study aimed to identify barriers and facilitators that affect access to HIV services for MSM. The online survey conducted this summer included 5779 men from 165 countries. In addition, the MSMGF collaborated with African Men for Sexual Health and Rights (AMSHeR) to conduct focus group discussions with a total of 71 MSM across five cities in South Africa, Kenya, and Nigeria.
Of men who participated in the online survey, only 35% reported that condoms were easily accessible, 21% reported easy access to lubricant, 36% reported easy access to HIV testing, and 42% reported easy access to HIV treatment. Levels of access differed across low-, lower-middle-, upper-middle- and high-income countries, with reduced access to services more commonly reported in lower-income countries.
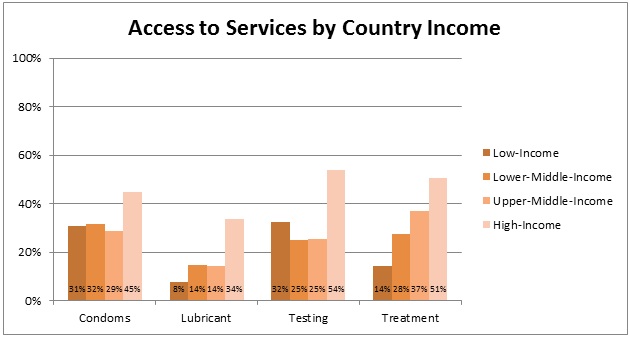 Percent of MSM reporting that condoms, lubricant, HIV testing, and HIV treatment
Percent of MSM reporting that condoms, lubricant, HIV testing, and HIV treatment
are easily accessible
(organized by country income level using World Bank country income classifications)
“Such poor levels of access at the global level are unacceptable,” said Dr. George Ayala, Executive Director of the MSMGF. “The differences in access by country income level are especially important to note as the Global Fund moves into a new funding model where countries are grouped into bands by income level. Even in upper-middle-income countries, MSM still have extremely low access to services. Without targeted funding to MSM and other key populations, the new funding model may continue to deteriorate levels of access for the groups most affected by HIV.”
The MSMGF research team also conducted analyses to identify barriers (factors associated with lower access) and facilitators (factors associated with higher access) that impact the ability of MSM to obtain condoms, lubricant, HIV testing, and HIV treatment.
Adjusting for country income, greater access to condoms, lubricants and HIV testing were associated with less homophobia, greater comfort with health providers, and more community engagement. Among participants living with HIV, higher access to HIV treatment was associated with less homophobia and greater comfort with service providers. Greater access to lubricants and greater access to HIV testing were also associated with less outness (the degree to which others know of one’s sexual orientation) and fewer negative consequences as a result of being out, respectively.
“As we collectively forge ahead into the new territory of treatment-based prevention, it is clear that many of the old challenges remain,” said Noah Metheny, Director of Policy at the MSMGF. “Addressing structural barriers remains essential to realizing the potential of HIV interventions for MSM, and it becomes more important with each new prevention and treatment option that is made available. Investments in the development of new interventions must be accompanied by efforts to increase access.”
The quantitative data from the online survey was supplemented with qualitative data from focus group discussions, helping to place barriers and facilitators in the broader context of the sexual health and lived experiences of MSM. Focus group discussion participants identified barriers and facilitators that were highly consistent with those found in the online survey, and many participants explained the ways that structural barriers at the policy, cultural, and institutional levels cascade down through the community and individual levels to block access to services for MSM.
Focus group discussion participants described how structural barriers like stigma, discrimination, and criminalization force MSM to hide their sexual behavior from health care providers, employers, landlords, teachers, and family members in order to protect themselves and maintain a minimum livelihood. The inability of MSM to reveal their sexual behavior to health care providers was linked to misdiagnosis, delayed diagnosis, and delayed treatment, leading to poor health prognosis and higher risk of transmitting HIV and other sexually transmitted infections to partners.
Conversely, focus group discussion participants explained that the negative consequences of structural barriers were moderated by the existence of safe spaces to meet other MSM, safe spaces to receive services, access to competent mental health care, and access to comprehensive health care. Participants described MSM-led community based organizations as safe spaces where they could celebrate their true selves, receive respectful and knowledgeable health care, and in some cases receive mental health services.
“The study’s findings underscore the urgent need to improve access to essential HIV services for gay men and other MSM worldwide,” said Dr. Ayala. “Interventions must both disrupt the negative effects of barriers and bolster the protective effects of facilitators. Study participants clearly indicated that community engagement and community-based organizations are central to moderating barriers and facilitating service access. Successfully addressing HIV among MSM will require a real effort to address structural barriers, and the findings from this study suggest that investing in MSM-led community-based organizations may be the best way to do that.”
Agreed. MSM-led community-based organizations must continue to work tirelessly to eliminate fear, shame, stigma and ignorance. They are all still very much with us.
And they’re killing us.
Related articles





